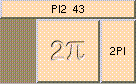
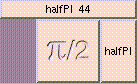
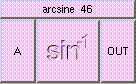
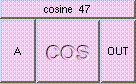
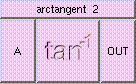
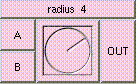
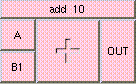
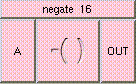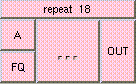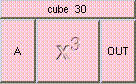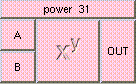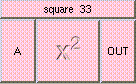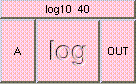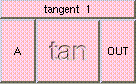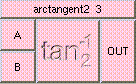ADD
Click box to see full description
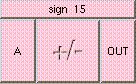
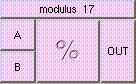
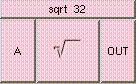
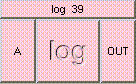
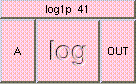
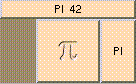
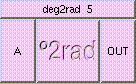
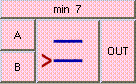
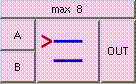
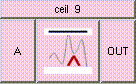
This is the addition function. The result is A + B + .... A and B may be scalar, vectors, or colors. The result will be a scalar if both A and B are scalars. The result will be a vector if either A or B is a vector. The result will be a color if either A or B is a color. A type mis-match will result from the addition of vectors and colors.